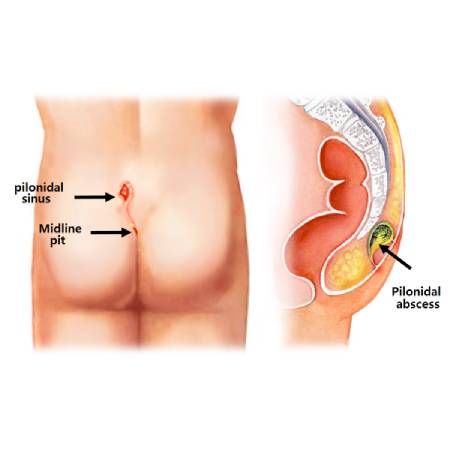
What is a Pilonidal Sinus?
A pilonidal sinus is a small tunnel or tract that forms in the skin, usually in the crease between the buttocks (near the tailbone). It may contain hair, debris and skin tissue, and can become infected, leading to pain, swelling, pus discharge and abscess formation. Pilonidal sinus is more common in young adults, especially males and often affects people who sit for long periods or have coarse body hair.
What causes a Pilonidal Sinus?
A pilonidal sinus typically develops when loose hairs penetrate the skin, causing the body to treat them as foreign objects. This triggers an inflammatory response, which can lead to the formation of a cyst or abscess. Common causes and risk factors include:
- Ingrown hair or hair follicles
- Prolonged sitting or friction in the buttock area
- Poor hygiene or excessive sweating
- Obesity
- Family history of pilonidal disease
- Wearing tight clothing or sitting for long hours
What are the symptoms of a Pilonidal Sinus?
Pilonidal sinus symptoms may vary depending on whether the condition is infected or chronic. Key signs include:
- Pain or tenderness near the tailbone
- Swelling or a lump at the top of the buttocks
- Pus or bloody discharge from a small opening in the skin
- Foul-smelling fluid or persistent drainage
- Redness and warmth around the area
- Fever (in cases of severe infection or abscess)
How is a Pilonidal Sinus diagnosed?
A pilonidal sinus is usually diagnosed through a simple physical examination. The doctor may inspect the area for signs of infection, pus discharge or the presence of sinus openings. In rare or complex cases, imaging tests like ultrasound or MRI may be used to assess the depth of the tract and plan surgical treatment if needed.
How can a Pilonidal Sinus be treated?
Treatment for pilonidal sinus depends on the severity and stage of the condition. Initial care may include good hygiene, warm sitz baths and antibiotics for infections. If an abscess develops, incision and drainage is often needed. For chronic or recurring cases, surgical options like excision or modern laser therapy provide effective, long-term relief. Additionally, Ayurvedic treatments such as Kshar Sutra offer a natural, minimally invasive alternative to promote healing and prevent recurrence.
What are the medical and surgical options?
- Incision and Drainage (I&D): A quick procedure to drain pus in case of an abscess.
- Excision Surgery: Complete removal of the sinus tract under local or general anesthesia.
- Laser Pilonidal Sinus Treatment: A modern, minimally invasive procedure that uses laser energy to close the tract with less pain, minimal scarring, and quicker recovery.
- Flap Surgery (for recurrent cases): Skin flap techniques may be used to close the area and reduce recurrence risk.
Is there an ayurvedic treatment for Pilonidal Sinus?
Yes. Ayurveda approaches pilonidal sinus (called Nadi Vrana) through:
- Kshar Sutra Therapy: A medicated thread is placed inside the sinus tract, promoting gradual healing and drainage.
- Herbal preparations and anti-inflammatory oils are used to cleanse the wound and prevent recurrence.
- Lifestyle guidance is also provided to maintain hygiene and prevent future infections.
Ayurvedic treatment offers a non-surgical option for patients seeking natural and effective care with minimal downtime.